The national database of state and local wildfire hazard mitigation programs
serves as a clearinghouse of information about nonfederal policies and
programs that seek to reduce the risk of loss of life and property through
the reduction of hazardous fuels on private lands. If
you would like to submit a program to the national wildfire programs database,
please complete the following form (MS
Word).
Return to your search results or Perform a new search
|
Title: |
Prescott, AZ-- UWI Code and Fuels Treatment Program
|
|
Type: |
Regulatory
Property Insurance
Homeowner assistance
Designation of high risk areas
|
|
Jurisdiction: |
City/town
|
|
State: |
Arizona
|
|
Program Description: |
Background
The Prescott Basin averages roughly 300 fires per year, split fairly evenly between lightning and human-caused ignitions. Assessed value of property at-risk in 2000 was $1.7 billion and included 14,000 homes.
The Prescott Vegetation Management Program was initiated in 2001. A collaborative approach was utilized by the Prescott Fire Department (Department) in developing an Urban -Wildland Interface Code. Numerous meetings were held to involve all stakeholders including city and county officials, contractors, landscape designers, insurance representatives, and homeowners.
The Program began with the passage of two ordinances that adopted the International Fire Code�s, 2000 Urban-Wildland Interface Code, with amendments. Subsequently, Ordinance 4367 was enacted to adopt the International Code Council�s, 2003 International Urban-Wildland Interface Code, with certain amendments. The latter enactment superseded the earlier ordinances.
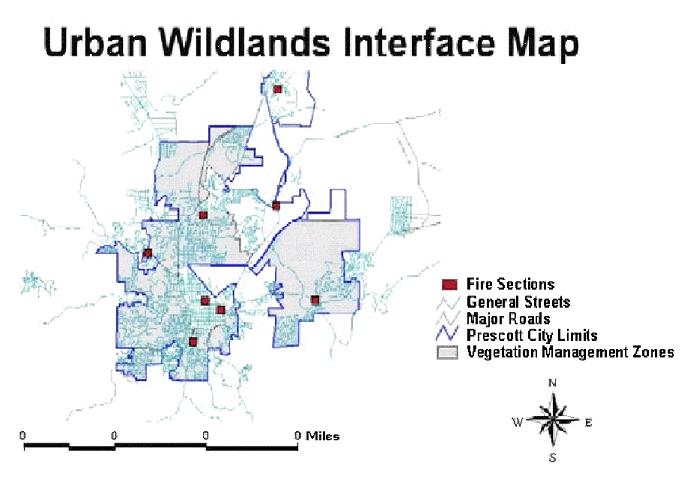
Hazard Assessment and Mapping
A fire hazard assessment was conducted by the Department using the NFPA 1144 rating system to delineate high fire hazard vegetation zones within the City based on fuel types, access, infrastructure and topography. The Department anticipates using RedZone software to assess properties and create a multi-layered database and mapping system in the future. Potential GIS layers include construction materials, access, fuel types, proximity of fuels to structures, location of water sources, placement of utilities, and specific mitigation actions recommended for the homeowner.
Fire Protection Plan Requirements
All new construction within high hazard zones requires a fire protection plan to address specific conditions in the area to be developed. Components of fire protection plan include 1) a copy of the site plan, 2) methods and timetables for modifying areas on the property, 3) a plan for maintaining defensible space. Plans are approved on an individual basis by the Fire Chief.
UWI Code Requirements
The Vegetation Management Plan (VMP) requirements of the UWI code apply to new construction whether in new or existing subdivisions if located within the wildland interface mapped area (see below). The requirements do not apply to existing homes in established subdivisions.
The VMP utilizes a 3-zone approach for defensible space. Defensible space is defined as the area between a house and an oncoming wildfire where the vegetation has been modified to reduce the wildfire threat and to provide an opportunity for firefighters too effectively defend the house. The VMP states that the defensible space shall be maintained at least annually.
In brief, the standards are as follows:
Zone 1. 0 -10 feet from buildings, structures, decks, etc.
- Remove native brush from under trees.
- Trim all trees to where the lowest branches or canopy are above the roofline.
- Tree canopies shall be a minimum of 10 feet apart.
- Trim or prune shrubs/vegetation to a maximum height of 2 feet and provide a clear space around each plant of a least 4 feet.
- Remove all dead materials.
- Cut grasses to a maximum height of 4 inches above the ground level.
- Remove all combustible materials and vegetation from under decks.
- Remove native brush and grass within 3 feet of buildings, structures, and decks.
- Optional planting of fire resistive vegetation shall be irrigated.
Zone 2. 10-30 feet from buildings, structures, decks, etc.
- Remove all ladder fuels by trimming, pruning up or removing vegetation under trees.
- Trim tree limbs a minimum of 6 feet from the ground.
- Tree canopies shall be a minimum of 10 feet apart.
- Remove dead material and remove/thin shrubs so that a person can walk between them.
- Cut grasses to a maximum of 4 inches above the ground level.
- Where vegetation is greater than 4 feet in height, create a clear space around each plant (or group of plants), twice the height of the plant in width.
- On slopes greater than 20% gradient, vegetation treatment shall be extended an additional 100 feet to a total of 130� from the structure, or to the property line.
- Remove the top or most recent layer of undecomposed needles or leaves.
Zone 3. 30-150 feet from building, structures, decks, etc where no slopes exist.
- Remove all ladder fuels by trimming, pruning up or removing vegetation under trees.
- Remove all dead materials.
All vegetation fuel modifications shall extend to the property line, where required. For a complete description of the requirements, see the VMP website.
In addition to the VMP requirements, Ordinance 4367 contains provisions for irrigation design and performance criteria in it�s Appendix B-2, as well as parameters for per acre tree density based on hydration in Appendix B-3.
Code Enforcement
Prior to obtaining a permit for construction, the builder must comply with the VMP requirements for defensible space within 30 feet of the structure (Zones 1 and 2). Implementation of defensible space standards from 30 to 150 feet of the structure (zone 3), are required prior to the issuance of an Occupancy Permit.
The Department has not initiated a citation program, however, non-compliance with the UWI Code will result in a hold on the construction permitting process. Department wildfire managers reported that the UWI Code has been well accepted in the community. In their view, this is due in large part to the efforts to involve all stakeholders in the Code development from the outset.
Insurance
Insurance companies are using Prescott Fire Department�s inspection reports for individual homes to evaluate wildfire risks; the level of risk determined may affect insurance rates and availability. However, homeowners are given two years to comply with the risk reduction steps recommended.
Homeowner Assistance
Since 2001, the Department has conducted fuels treatment on more than 3,000 properties. A 10-person crew assists homeowners in reducing vegetation on their property including chipping and slash removal if the homeowner if unable to mange the treatment themselves. The cost is $100 per property. These treatments have been funded through grants from the, Prescott Area Wildland-Urban Interface Commission. Department fire managers reported that initially, some homeowners were reluctant to reduce fuels. However, once a few treated properties were viewed, the residents adopted a much more �firewise mindset�.
Contacts
For more information, contact Ted Galde at [email protected] or Jeremy Brinkerhoff at [email protected]
|
|
Images: |
|
1. | 
|
|
|
|
|